The new microservice accelerates novel materials discovery to help developers and researchers speed the renewable energy transition.
More than 96% of all manufactured goods — ranging from everyday products, like laundry detergent and food packaging, to advanced industrial components, such as semiconductors, batteries and solar panels — rely on chemicals that cannot be replaced with alternative materials.
With AI and the latest technological advancements, researchers and developers are studying ways to create novel materials that could address the world’s toughest challenges, such as energy storage and environmental remediation.
Announced today at the Supercomputing 2024 conference in Atlanta, the NVIDIA ALCHEMI NIM microservice accelerates such research by optimizing AI inference for chemical simulations that could lead to more efficient and sustainable materials to support the renewable energy transition.
It’s one of the many ways NVIDIA is supporting researchers, developers and enterprises to boost energy and resource efficiency in their workflows, including to meet requirements aligned with the global Net Zero Initiative.
NVIDIA ALCHEMI for Material and Chemical Simulations
Exploring the universe of potential materials, using the nearly infinite combinations of chemicals — each with unique characteristics — can be extremely complex and time consuming. Novel materials are typically discovered through laborious, trial-and-error synthesis and testing in a traditional lab.
Many of today’s plastics, for example, are still based on material discoveries made in the mid-1900s.
More recently, AI has emerged as a promising accelerant for chemicals and materials innovation.
With the new ALCHEMI NIM microservice, researchers can test chemical compounds and material stability in simulation, in a virtual AI lab, which reduces costs, energy consumption and time to discovery.
For example, running MACE-MP-0, a pretrained foundation model for materials chemistry, on an NVIDIA H100 Tensor Core GPU, the new NIM microservice speeds evaluations of a potential composition’s simulated long-term stability 100x. The below figure shows a 25x speedup from using the NVIDIA Warp Python framework for high-performance simulation, followed by a 4x speedup with in-flight batching. All in all, evaluating 16 million structures would have taken months — with the NIM microservice, it can be done in just hours.
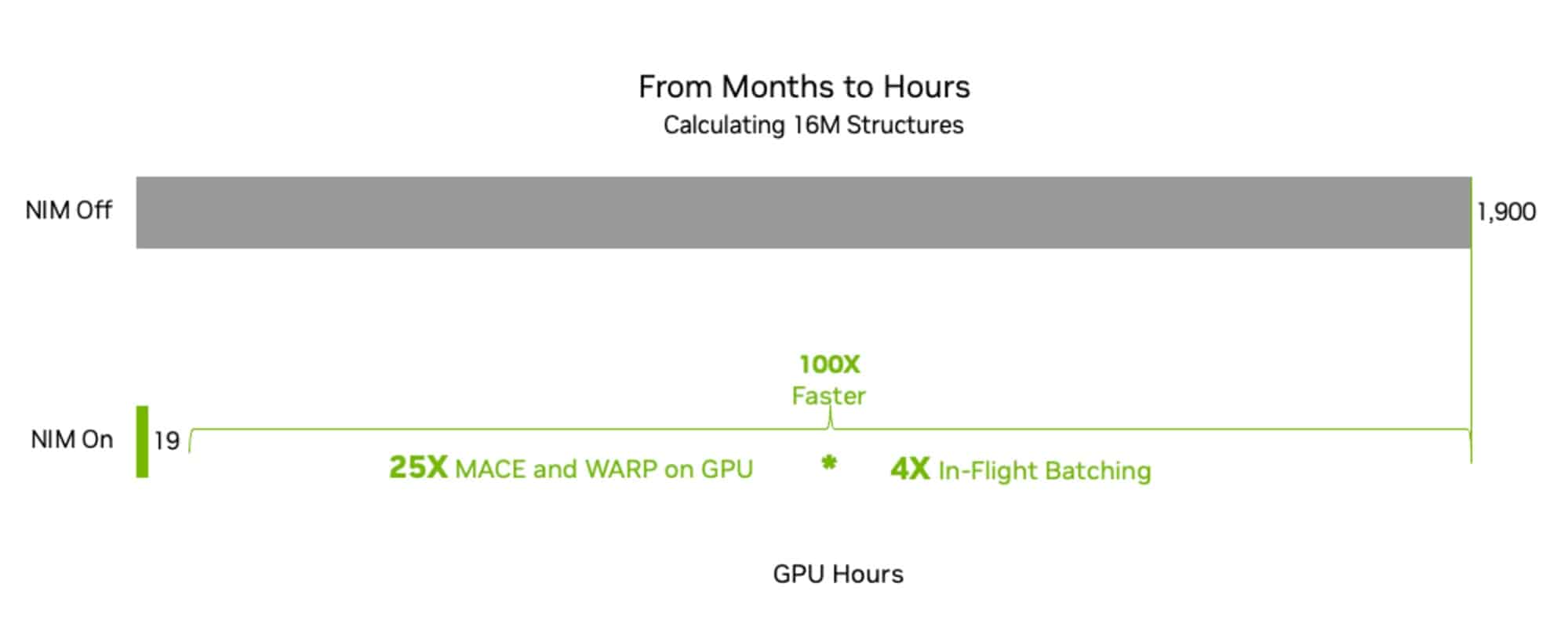
By letting scientists examine more structures in less time, the NIM microservice can boost research on materials for use with solar and electric batteries, for example, to bolster the renewable energy transition.
NVIDIA also plans to release NIM microservices that can be used to simulate the manufacturability of novel materials — to determine how they might be brought from test tubes into the real world in the form of batteries, solar panels, fertilizers, pesticides and other essential products that can contribute to a healthier, greener planet.
SES AI, a leading developer of lithium-metal batteries, is using the NVIDIA ALCHEMI NIM microservice with the AIMNet2 model to accelerate the identification of electrolyte materials used for electric vehicles.
“SES AI is dedicated to advancing lithium battery technology through AI-accelerated material discovery, using our Molecular Universe Project to explore and identify promising candidates for lithium metal electrolyte discovery,” said Qichao Hu, CEO of SES AI. “Using the ALCHEMI NIM microservice with AIMNet2 could drastically improve our ability to map molecular properties, reducing time and costs significantly and accelerating innovation.”
SES AI recently mapped 100,000 molecules in half a day, with the potential to achieve this in under an hour using ALCHEMI. This signals how the microservice is poised to have a transformative impact on material screening efficiency.
Looking ahead, SES AI aims to map the properties of up to 10 billion molecules within the next couple of years, pushing the boundaries of AI-driven, high-throughput discovery.
The new microservice will soon be available for researchers to test for free through the NVIDIA NGC catalog — be notified of ALCHEMI’s launch. It will also be downloadable from build.nvidia.com, and the production-grade NIM microservice will be offered through the NVIDIA AI Enterprise software platform.
Learn more about the NVIDIA ALCHEMI NIM microservice, and hear the latest on how AI and supercomputing are supercharging researchers and developers’ workflows by joining NVIDIA at SC24, running through Friday, Nov. 22.
See notice regarding software product information.
https://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/alchemi-nim/?ncid=so-face-686453





