The banking ecosystem continues to evolve, with several emerging themes that will play significant roles in the transformation of both new and traditional financial services businesses. These trends should provide the foundation for strategic planning and for the prioritizing of investments in the near term.
Over the past decade, fintech firms have leveraged technology, innovative cultures and access to data and advanced analytics to transform the banking ecosystem. While the success of individual fintech firms varied widely, the solutions have impacted payments, infrastructure, distribution, access to financial services and components of sustainability.
Initially, many of these fintech solutions were viewed as competitive threats to traditional banking providers. While many of the largest and fastest growing fintech firms (and big tech platforms) continue to directly impact the business models of legacy banks and credit unions, there is an increasing trend to collaborate with fintech providers for faster deployment of digital solutions desired by consumers and businesses.
The willingness of consumers to try new digital financial services grew exponentially as a result of the pandemic, increasing the speed of innovation within the banking industry. With the access to branches shut down, both traditional and non-traditional financial services providers needed to respond to the need for fast, seamless solutions that made banking easier. Almost immediately, legacy back-office processes had to be rethought to support solutions that replicated those already provided by fintech providers.
Given this pace of change, it is important to be aware of some of the major themes that are impacting the banking industry. By understanding where the greatest level of activity is within the fintech marketplace, banks and credit unions can set priorities for the short and mid-term. Speed of innovation is at the core of digital banking transformation – where the question is not whether change will occur, but which changes are the biggest threats (and opportunities) to existing business models.
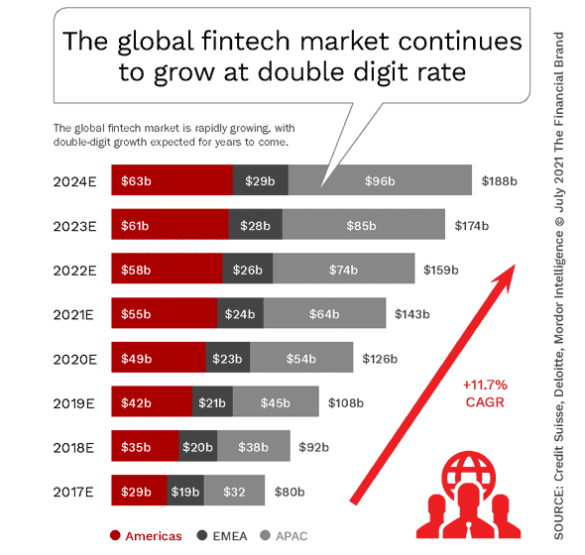
The major digital transformation themes below are neither prioritized nor exhaustive in nature. Most of these trends directly impact the delivery of retail banking products and services. All of these trends (and others) must be taken into account as strategic planning processes are beginning, and each has a heightened level of urgency as consumer and business banking behaviors continue to change. (For additional trends and a deeper dive into many of these themes, see research from Credit Suisse)
1. Faster, Omnichannel Payments
In no area of banking has innovation been more significant than in payments. Payments are becoming faster, more secure and more embedded into every part of our lives, as consumers expect to be able to execute a transaction with a push of a button on their mobile device.
While the transformation of payments differs across different regions, the trend towards faster (same day or real-time) is universal. According to Credit Suisse, “Faster payments is enabling individuals to be paid faster, businesses to have greater control over working capital, and is a step toward eliminating batch processing systems within financial institutions and potentially revolutionizing the correspondent banking system.”
With traditional forms of in-person retail commerce shut down due to the pandemic, the importance of being able to support transactions in a contactless manner became a necessity. The use of data and analytics to drive digital media campaigns and to enhance the customer journey has become table stakes. Most businesses are looking to their financial services provider to assist them with creating value-added omnichannel solutions.
2. New Payment Innovations
Not only has the speed of payments been impacted, but the speed of payments innovation is increasing. Solutions like Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) have gained popularity almost overnight, creating a unique form of real-time point-of-sale financing. This new innovation has forced traditional banks and even competing payment providers to play catch-up. While most solutions are for short-term deferred payments, new alternatives have been created for larger purchases with longer-term installments. As a result, BNPL has impacted not just debit issuers, but also credit card and personal loan providers.
As has been seen in other financial product areas, new payment innovations often have emerged faster than the regulations to protect consumers. As regulators sort through the risks to consumers associated with new solutions, financial institutions have an opportunity to create competing solutions with improved transparency and better risk/reward models.
3. Open Banking
Open Banking has become one of the most important global trends in the banking ecosystem. Originated in the U.K., the concept lowers barriers to entry for alternative financial services providers and enhances the potential for innovation by mandating traditional financial institutions to share financial data through APIs. While the extent of regulated sharing differs across countries, the potential for new products and services both within and outside traditional financial services is enormous.
Opening the door to unique collaborations, the ability to use customer insight for personalized and contextual solutions has also opened the door for developers to build solutions with completely new revenue models that may not rely on financial products alone. Many incumbent financial services providers are also building new payment, savings, investment and financial wellness solutions independently and in collaboration with fintech providers.
4. Investment in Technology
If there is a single dimension of digital banking transformation that differentiates the large banks and newer fintech players from the regional and smaller legacy providers it is the investment in modern technology. While investment in technology is not the only requirement for becoming a successful digital provider, it is certainly an important component.
With most fintech and big tech providers being built on modern digital infrastructure, it is a mission for most traditional financial institutions to prioritize the technology that is needed to make the biggest impact to compete with these digital-native alternatives. Most mid-sized and smaller organizations (as well as some of the largest banks) have either modernized portions of their back-office and/or have partnered with solution providers, including fintech firms, who can build agile digital solutions at speed. The question is whether small and mid-sized financial institutions can remain competitive in such a fast moving environment.
5. Outsourced Solutions
As mentioned, many financial institutions are hoping to keep pace with change by collaborating with fintech providers and third-party developers. This provides the benefit of tested solutions and implementation speed that would not be possible if an in-house solution was pursued. This strategy is also being used by fintech firms who want to expand their product offerings beyond a single solution or want to utilize established back-office technology from legacy banking organizations.
When hoping to build an improved new account opening or digital lending process, or add a new solution to the product mix, working with organizations that have already built a viable solution for other institutions is a great option. It allows for focus to be moved to other initiatives that may need greater internal resources.
6. Embedded Banking and Platforms
The future of financial services extends beyond historical delivery mechanisms and traditional products and services. The expansion of the use of data and applied analytics has enabled the embedding of banking services such as payments, deposit and lending within non-financial solutions. The result is that consumers and small businesses are realizing they do not need to go to traditional providers to get their financial needs met. The value-add is usually the use of insights to optimize the engagement.
An extension of the concept of embedded financial services is the development of ‘super apps’ that go beyond traditional financial services to drive higher engagement and loyalty while improving overall customer experiences. These marketplace solutions often have a hub around deposit services (checking), eCommerce, lending or payments, and generate revenue within and outside of financial solutions.
7. Specialized Digital Lenders
If there is a single area where legacy banking organizations fall short of consumer expectations it is digital lending. In the majority of cases, the processes are slow and paper-based, not changing significantly over the past several decades. At a time when consumers expect all of their digital engagements to be fast and easy, borrowing at a traditional bank or credit union is painful and time consuming.
The result of this broken process has been the emergence of specialized lenders that can process mortgages, auto loans, personal loans, student loans and even credit cards far more efficiently than in the past. This has resulted in an unprecedented shift of market share away from traditional banks to fintech players that leverage a laser focus on experience, modern technology, marketing acumen and low cost acquisition models to deliver digital loans at scale.
With the ability to deliver approvals in seconds and close loans in a fraction of the time, physical interaction is avoided and loyalty is created. In fact, with the importance of the traditional checking account decreasing, the potential for digital lenders to shift a ‘primary relationship’ with the addition of some ancillary services should concern any legacy banker.
8. Personalized Engagement Across Customer Journey
With a focus on data, analytics and modern technology, neobanks/challenger banks and other fintech firms have been able to increase ongoing engagement across the customer journey by providing contextual communication and offers that highlight personalization of experiences. With more consumers using digital channels, the ability to reach customers with highly customized social media, digital marketing and mobile app messaging far exceeds the communication usually delivered by legacy banks and credit unions.
The pandemic heightened the need to build personalized engagement similar to what is provided by Apple, Amazon, Google, Facebook, Netflix and other digital-first organizations. With consumers indicating an increasing willingness to use multiple financial services providers, and with fintech providers being increasingly adept at digital marketing, legacy relationships (and ultimately the foundation accounts) are put at risk.
Prioritize for the Future
The tens of thousands of fintech organizations in the marketplace provide a fantastic springboard for analysis and discussion of potential paths for future growth. By looking at the major trends in the marketplace, and either building innovative competitive solutions, or defending current turf, legacy banks and credit unions must prioritize where there is greatest potential for future success.
In some cases, an organization may build solutions internally, while others will partner with fintech firms or solution providers to meet the needs of customers. No matter which path is chosen, speed of implementation is key.
It is anticipated that M&A activity will escalate both within the banking industry and among fintech firms as organizations seek scalability and financial viability. As stated by Credit Suisse in their report, “Given the fragmented nature of the market and the significant economies of scale present in nearly all sub-industries within fintech, consolidation seems likely, although activity could remain muted in the near-term depending upon valuations and public company willingness to make temporarily dilutive acquisitions.”
https://thefinancialbrand.com/117459/digital-banking-fintech-transformation-trends-payments-technology-marketing/