China Mobile claims that the Next Gen. Mobile Networks Alliance, a global group of mobile network operator companies, recently fully released the white paper “6G Needs and Design Considerations”. This paper is co-led by China Mobile, Vodafone, and US Cellular. 53 global firms, including 23 device makers and 13 research institutes, took part in the initiative. At the moment, there are no less than 17 operators leading the group around the world.
The WP5D working group of the International Telecommunication Union Radiocommunication Group is urged to create a 6G vision through the release of the white paper. It focuses on 6G needs and design concerns. The white paper gives tips for 6G system design and structure issues. It also defines 6G needs from the operators’ point of view. This includes the history path needs for digital inclusion, energy efficiency, environmental sustainability, and flexible deployment. It is known that the progress from 5G to 6G is a process from IoT to “Intelligent Connectivity of Everything, Digital Twin,”. From the reports so far, the capacity of the 6G network will be 10 times faster than the 5G network.

6G network to have several use cases
There will be a lot of usage scenarios for the super fast 6G network. The White Paper reveals that it will promote the holographic video with a better sense of use. There will be a more realistic link between the virtual and physical worlds. However, there is no need for too much excitement at the moment. There is still a lot of work to be done. At the moment, the 6G network is still in its infancy. By 2030, we expect that this network should be usable. It is worth noting that 2030 is still a long time away so a lot can change before then.

The unique design of 6G network is highly valued by the Chinese govt. The IMT-2030 (6G) Promotion Group was set up in 2019 by the MIIT and the NDRC to actively boost various tasks like needs, techs, standards, and global cooperation. The group also launched 6G network tech trials.
If the 2G network is equated to a bullock cart, the 3G network to a bicycle, the 4G network to a car, and the 5G network to a high-speed rail, then the 6G network is an aeroplane. This is according to China Telecom’s official Weibo handle.
History of the telecommunication network
The history of the cell phone network can be traced back to the 1940s and 1950s. This is when the first mobile radio systems were developed for use in vehicles. However, these systems were expensive and primarily used by govt agencies and large companies.
1G network
The first gen. of mobile networks, or 1G, was introduced in the 1980s. These networks were analog and provided only basic voice calling services. The first commercial 1G network was launched in Japan in 1979 by NTT. 1G networks used frequency-division multiple access (FDMA) techs. This divided the available frequency spectrum into different channels for voice transmission.
Gizchina News of the week

1G networks had limited coverage and were expensive to use. This did not help the use of this network. On top of that, the call quality was also poor. There were also very high risks of eavesdropping due to the lack of encryption. 1G networks did not support any data services or text messaging.

Despite these limits, 1G networks were a significant step forward in mobile communications, as they provided users with the ability to make calls while on the move. 1G networks paved the way for the development of the digital cellular network, or 2G, which was introduced in the early 1990s and offered improved call quality and the ability to send text messages.
2G Network:
The second generation of mobile networks, or 2G, was first introduced in the early 1990s. These networks were digital, which improved call quality and reduced interference, and allowed for text messaging. The most widely used 2G standard was Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM). 2G networks typically offered data speeds of up to 50 kbps, which was sufficient for basic internet browsing and email.

3G Network:
The third generation of mobile networks, or 3G, was introduced in the early 2000s. 3G networks provided faster data speeds, improved call quality, and introduced new features such as video calling and mobile internet access. The most widely used 3G standard was Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS). 3G networks typically offered data speeds of up to 2 Mbps, which allowed for more advanced services such as mobile video streaming and mobile gaming.
4G Network:
The fourth generation of mobile networks, or 4G, was introduced in the late 2000s. 4G networks provided even faster data speeds, improved call quality, and introduced new features such as voice-over internet protocol (VoIP) and mobile hotspots. The most widely used 4G standard was Long-Term Evolution (LTE). 4G networks typically offered data speeds of up to 100 Mbps, which allowed for high-quality video streaming and online gaming.
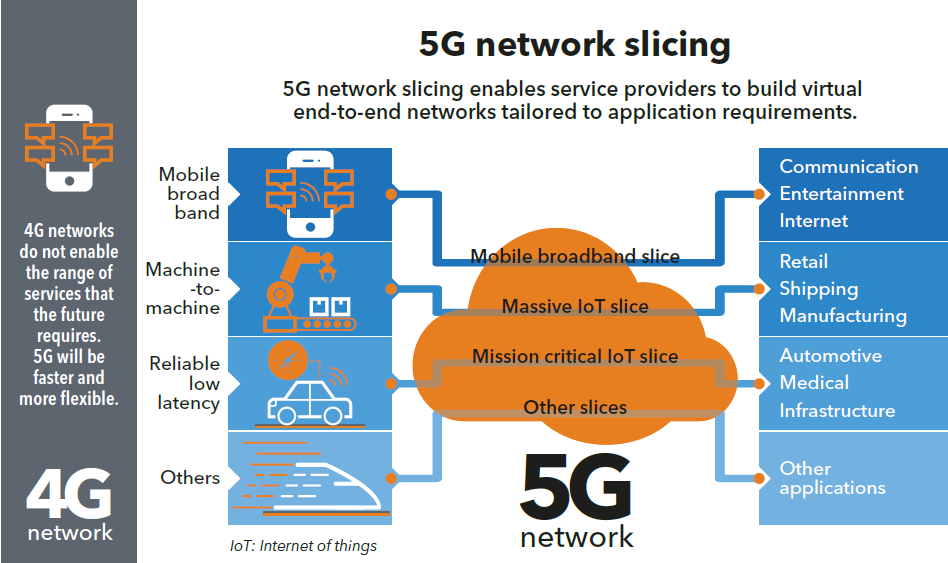
5G Network:
The fifth gen. of mobile networks, or 5G, is currently being rolled out around the world. The 5G network promise to provide even faster data speeds, lower latency, and improved reliability. It uses advanced techs such as millimetre-wave (mmWave) and massive multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) to achieve these improvements. 5G networks are expected to offer data speeds of up to 20 Gbps, which will enable new services such as augmented reality and virtual reality. 5G networks will also be capable of supporting a large number of devices, which will enable the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart cities.
https://www.gizchina.com/2023/03/22/6g-network-capacity-is-10x-that-of-5g-network/amp/





