Insider Brief
- The Quantum Economy Landscape in Saudi Arabia report offers an in-depth analysis of how the Kingdom is is pursuing a leadership role in quantum technology as part of its Vision 2030 plan to diversify the economy and drive innovation.
- The Kingdom focuses on education, research, and partnerships to build a quantum ecosystem, highlighted by collaborations with global leaders like IBM and Pasqal.
- Key challenges include the need for more talent and limited infrastructure, but strategic plans emphasize education, infrastructure and international collaboration to bridge these gaps.
Saudi Arabia is positioning itself to become a major player in quantum technology, a scientific revolution expected to transform industries ranging from healthcare to cybersecurity.
Experts from The Centre for the Fourth Industrial Revolution in Saudi Arabia recently released its Quantum Economy Landscape in Saudi Arabia report, which outlines the country’s progress, challenges and future roadmap for building a robust quantum ecosystem. The plan is guided by its Vision 2030 blueprint, which sets the Kingdom on a path to better diversify its economy and establish itself as a global innovation hub.
“This report marks a pivotal step towards charting a course for a national quantum roadmap harnessing quantum advancements, fostering innovation, and bolstering productivity across diverse industries, potentially revolutionizing the country’s technological and economic landscape,” the report states.
More Than Quantum Computing
Quantum technology harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics — a branch of physics that describes the behavior of particles at atomic and subatomic levels. The report breaks down quantum technology into five key areas:
- Quantum Computing: Solving problems beyond the reach of classical computers, such as molecular simulations for drug discovery.
- Quantum Communication: Providing secure data transmission using quantum key distribution (QKD).
- Quantum Sensing: Enhancing precision in applications like medical imaging and environmental monitoring.
- Quantum Cryptography: Strengthening cybersecurity by detecting eavesdropping in real time.
- Quantum Simulation: Modeling complex systems for industries like materials science and energy.
According to the report: “Quantum technology can drive innovation across multiple sectors, creating new industries and economic growth. It could lead to the development of new products and markets. As quantum technology advances, there will be a growing demand for skilled workers in quantum computing, chemistry, materials science and related fields, creating new job opportunities.”
These capabilities present vast opportunities but also bring challenges, particularly for nations aiming to secure a foothold in this rapidly evolving field.
Saudi Arabia’s Current Quantum Landscape
Saudi Arabia’s efforts in quantum technology are still in their infancy, yet the Kingdom has made significant strides in laying the groundwork for future advancements. The Quantum Economy Landscape report highlights a series of initiatives across research, education and commercialization.
Educational Efforts and Talent Pipeline
Developing a quantum-savvy workforce will be essential to Saudi Arabia’s ambitions. The Kingdom has adopted a three-phase approach:
- Early Engagement: Programs targeting primary and high school students remain limited but are seen as critical for building foundational interest in quantum science.
- University-Level Education: Institutions such as King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals (KFUPM) and King Abdullah University for Science and Technology (KAUST) offer specialized courses and research opportunities. These include a master’s program in quantum computing and a research group in quantum photonics.
- Professional Upskilling: Workshops, internships, and partnerships with global organizations aim to reskill industry professionals. For example, TUWAIQ Academy collaborates with entities like IBM to provide hands-on training.
The report also details challenges with building a quantum workforce. A limited pool of qualified educators and researchers, combined with global competition for talent, underscores the need for more robust long-term strategies.
Research and Innovation
Saudi Arabia’s research output in quantum technology has shown steady growth. Universities and research centers have launched initiatives to explore areas such as quantum computing, cryptography, and sensing. For example:
- KFUPM hosts advanced labs for quantum communication and high-performance computing.
- King Saud University’s Center of Excellence in Information Assurance focuses on post-quantum cryptography.
The Kingdom has also entered international partnerships to bolster its capabilities. In 2024, Saudi Aramco and Pasqal announced plans to deploy a 200-qubit quantum computer that would serve as a significant milestone in regional quantum hardware development.
Commercialization and Partnerships
Strategic collaborations between public and private sectors have been pivotal in advancing quantum technology. Highlights include:
- Aramco and IBM: Establishing an innovation hub in Saudi Arabia to explore industrial applications of quantum computing.
- NEOM and Arqit: Developing a quantum security system to protect futuristic cities from advanced cyber threats.
- C4IR Saudi Arabia and WEF: Launching the ‘Quantum for Society Challenge’ to encourage quantum solutions for global issues like climate resilience and healthcare.
The partnerships not only accelerate technological development but also create pathways for commercialization. They are also critical in transforming research into tangible economic value, the report states.
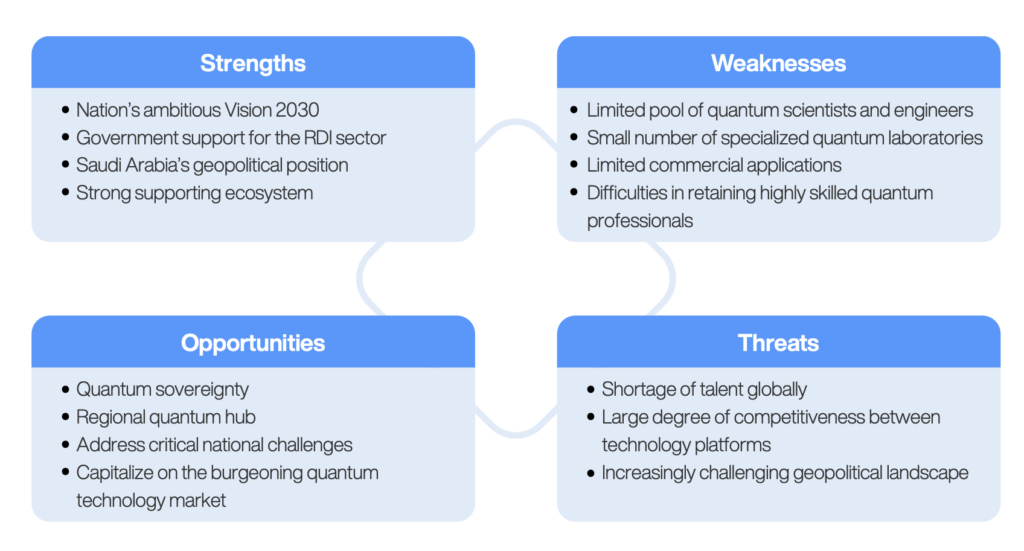
Challenges and Opportunities
Saudi Arabia’s ambitions are tempered by several challenges:
- Talent Shortage: The Kingdom’s limited pool of quantum scientists and engineers is a significant bottleneck.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Few specialized laboratories exist to support advanced quantum research.
- Global Competition: Established quantum leaders like the U.S. and China pose formidable competition in both talent acquisition and technological development.
However, the Kingdom’s strategic location, robust government support and Vision 2030 framework present unique opportunities. Saudi Arabia aims to position itself as a regional quantum hub, attracting investment and fostering collaboration across the Middle East.
A Roadmap for the Future
The report outlines a comprehensive roadmap for advancing Saudi Arabia’s quantum economy. Key recommendations include:
- Developing a National Quantum Agenda: A unified strategy to identify priority areas, allocate funding, and set long-term goals.
- Building Infrastructure: Establishing specialized facilities like a Quantum Foundry to support hardware innovation. This foundry would develop on-chip quantum technologies, leveraging the Kingdom’s existing semiconductor capabilities.
- Enhancing Education: Expanding STEM initiatives at all educational levels and introducing more accessible programs to democratize quantum learning.
- Fostering International Collaboration: Strengthening ties with global quantum leaders to share expertise and resources.
- Encouraging Public Awareness: Hosting events like World Quantum Day celebrations to engage the public and promote a quantum-literate society.
The opportunities are as great as the challenges, which requires careful planning and management.
The report states: “Quantum technologies have wide-ranging applications across sectors like healthcare, energy, finance, and logistics, spurring the creation of new products, markets, and jobs. Quantum communication enables highly secure networks to protect sensitive information from cyberattacks. Quantum imaging could enhance medical diagnostics, improve low-light detection, and advance nanotechnology. However, quantum computers may also pose security risks to existing classical infrastructure. To maximize benefits and minimize risks of quantum technologies, a comprehensive national program is crucial. This should be led by a governance consortium of key stakeholders from government, industry, and academia.”
Global Context and Comparisons
Saudi Arabia’s quantum journey should be viewed in the context of global efforts. Nations such as the U.S., China, and Germany have committed billions to quantum research, establishing national strategies and quantum hubs. For example:
- The U.S. National Quantum Initiative Act has allocated over $1.2 billion to projects involving institutions like IBM and Google.
- China’s investments in quantum communication and computing surpass $15 billion.
- Germany’s Munich Quantum Valley focuses on developing a fault-tolerant quantum computer by 2026.
While Saudi Arabia’s investments are modest in comparison, its focus on strategic partnerships and regional leadership positions it uniquely in the global quantum race.
Looking Ahead
As Saudi Arabia embarks on its quantum journey, it faces both significant challenges and transformative opportunities. By prioritizing education, fostering innovation, and building strategic partnerships, the Kingdom has the potential to emerge as a leader in the quantum economy, according to the report. The Quantum Economy Landscape report serves as a vital blueprint, charting a course toward a future where quantum technologies drive economic diversification, technological leadership, and societal progress.
The Centre for the Fourth Industrial Revolution in Saudi Arabia is a think tank to advance the benefits of C4IR in Saudi Arabia through the development and implementation of practical and adaptive protocols for the governance of emerging technologies.
Saudi Arabia Lays Out Its Strategic Vision For The Quantum Era






